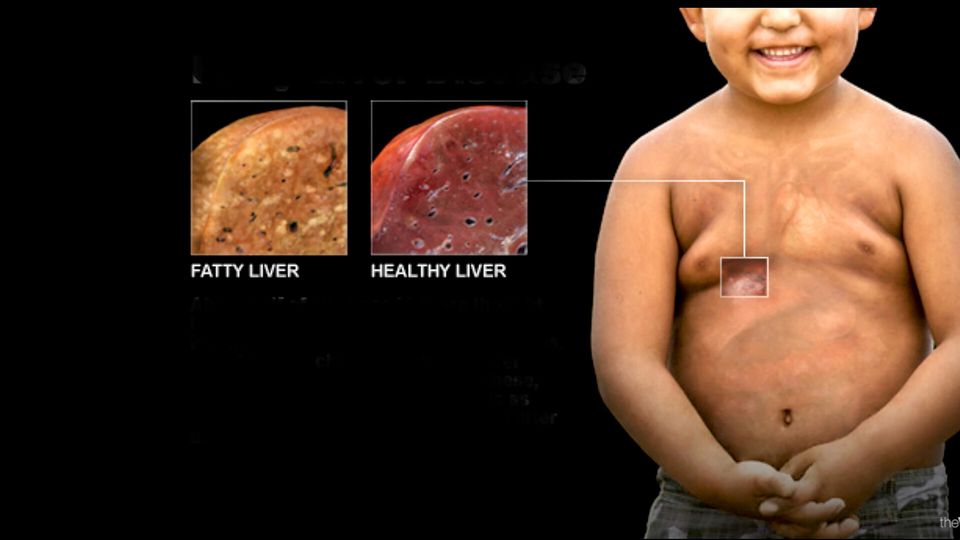
A troubling health trend has emerged among our youth: the increasing prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In the past, this disease was considered an adult condition. Today, NAFLD has become the most common liver disease in children, affecting a staggering 1 in 10 kids in the United States. This silent epidemic demands our attention and action.
NAFLD occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver, potentially leading to inflammation, scarring, and long-term liver damage. This is very concerning because this condition often shows no symptoms until significant harm has already occurred. Here are the statistics:
• The prevalence of NAFLD in children has more than doubled in the last 20 years.
• 17% of teenagers aged 15-17 are affected by NAFLD.
• A staggering 38% of children with obesity have NAFLD.
Several factors contribute to the development of NAFLD in children:
• Obesity: The primary risk factor, with 38% of obese children affected.
• Genetics: Hispanic and Asian American children are at higher risk.
• Metabolic syndrome: Including insulin resistance and abnormal blood lipid levels.
• Food insecurity: Latinx children from food-insecure households at age 4 are nearly four times more likely to develop fatty liver disease by age 12.
The biggest challenge is that these children often don’t experience any symptoms. They may not experience any discomfort or visible signs until the disease has progressed significantly. This underscores the importance of early screening and intervention.
Recent research has shed light on a crucial factor in the development of NAFLD in children: oxidative stress and its relationship with glutathione levels. A cross-sectional study involving children and adolescents aged 8-18 years revealed a significant association between reduced serum glutathione peroxidase (GPx) levels and NAFLD. Key findings from this study include:
• 24% of the studied children had NAFLD
• Children with NAFLD showed more frequent abdominal obesity
• NAFLD was associated with high body mass index/age and reduced serum GPx levels
• Oxidative stress markers correlated with various factors, including copper levels and interleukin-6This research underscores the importance of addressing glutathione deficiencies in the management of NAFLD in children. Glutathione, known as the ‘master antioxidant,’ plays a crucial role in protecting the body from oxidative damage and is highly concentrated in the liver.
This research underscores the importance of addressing glutathione deficiencies in the management of NAFLD in children. Glutathione, known as the ‘master antioxidant,’ plays a crucial role in protecting the body from oxidative damage and is highly concentrated in the liver . Reduced levels of glutathione have been associated with increased disease risk and progression, including NAFLD and other liver pathologies.
Immunocal, a whey protein isolate, offers a promising approach to addressing these glutathione deficiencies. Here’s how Immunocal can help:
- Precursor provision: Immunocal provides cysteine, a crucial precursor for glutathione synthesis, helping to boost the body’s natural production of this vital antioxidant.
- Antioxidant defense: By increasing glutathione levels, Immunocal may help combat the oxidative stress associated with NAFLD, potentially slowing disease progression.
- Liver function support: Enhanced glutathione levels may aid in reducing fat accumulation in the liver, addressing the root cause of NAFLD.
- Cellular health enhancement: Improved glutathione status promotes better overall metabolic function throughout the body, which is particularly important for children with NAFLD.
Preliminary studies have shown beneficial effects of supplemental glutathione in the treatment of NAFLD, demonstrating a reduction of ALT – a liver enzyme elevated in liver dysfunction and one of the principal NAFLD biomarkers – after four months of treatment. While more research is needed, especially in pediatric populations, these findings suggest that glutathione supplementation through products like Immunocal could be a valuable addition to NAFLD management strategies. While there’s no magic pill to cure NAFLD, it’s important to note that while Immunocal and glutathione supplementation show promise, they should be part of a comprehensive approach to managing NAFLD in children. This approach should include:
- A balanced, nutritious diet low in processed foods and sugars
- Regular physical activity, aiming for at least 60 minutes daily
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular medical check-ups and liver function monitoring
- Early screening for children with risk factors
The rise of NAFLD in children is a wake-up call for parents, healthcare providers, and policymakers. By promoting healthy lifestyles, ensuring access to nutritious foods, and implementing early screening programs, we can combat this silent epidemic and protect our children’s liver health for years to come. By combining lifestyle modifications with targeted nutritional interventions like Immunocal, we can take significant steps towards addressing the growing epidemic of NAFLD in children. However, it’s crucial to consult with healthcare professionals before starting any new supplement regimen, especially for children. With a multifaceted approach that includes addressing glutathione deficiencies, we can work towards better liver health outcomes for our youth. Remember, the liver has an incredible ability to regenerate and recover when given the chance. By taking action now, we can help our children avoid the long-term consequences of NAFLD and set them on a path to lifelong health and well-being.
STUDY: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39446125/
STUDY: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3016512/
ARTICLE: https://www.childrens.com/health-wellness/fatty-liver-disease-in-children-on-the-rise